A Brief Discussion On the Adhesion of Powder Coatings
Powder coating is an important part of modern coating industry, it is used in cast iron, cast aluminum, stainless steel, galvanized, aluminum magnesium alloy, from the ordinary thermosetting powder coating to special functional powder coating, heavy anticorrosive powder coating, aluminum profile special, and People's Daily life and high-tech science and technology are closely related. Adhesion is one of the basic mechanical properties of powder coatings. Shanghai qungrun technology co., LTD.
1、Factors Affecting Adhesion
Adhesion is created when two objects are brought together to a tight interface where molecular contact creates a new interface layer.
1.1 The Surface Wettability
The wetting process is related to the interfacial tension of the system. Only by reducing the surface tension can the wetting efficiency be improved and the adhesion of the coating to the surface metal be increased.
1.2 Mechanical Bite
Mechanical bite force is one of the most direct forces, people since ancient times to connect two objects in this way. In the submicroscopic state, most of the substrate surface is rough. Adhesive or melt with good flow performance flows in and fills these holes and depressions. After drying and curing, mechanical bite force such as hook anchor, tenon and riveting is formed. The roughness of the surface affects the surface area of the coating and substrate. Since the force required to remove the coating is related to the geometric area, the force required to make the coating adhere to the substrate is related to the actual interface contact area. As the surface area increases, the difficulty of removing the coating increases, which can usually be achieved by providing a rough surface with a mechanical grinding method. Adhesion is beneficial only when the adhesive or coating can penetrate the irregular interface of the rough surface. If cannot or infiltration is not sufficient, the contact between coating and surface can be smaller than the corresponding geometric area, and leave a gap between coating and substrate, the gap will lead to the accumulation of water vapor, ultimately leading to the loss of adhesion. This is related to the phenomenon of capillary rise, the contact Angle is an acute Angle, the infiltration of liquid rise; The contact Angle is obtuse and does not infiltrate the liquid. If adhesive or coating in the surface of the substrate contact Angle is greater than 90 degrees, even if there is a grinding, a higher roughness, bonding strength will not be very strong. If want to bond nonpolar plastics like polyethylene, ptfe, etc., because their surface energy is low, lower than the adhesive or coating, even if coated up, it is difficult to achieve a close interface contact, at the same time in the interface there will be stress on the adhesion of the durability. Therefore, in order to improve the adhesion of plastic surface, usually corona discharge treatment, mechanical and chemical grafting, or other oxidation introduced polar groups, so as to improve the surface energy.
1.3 Chemical Bonds
Chemical bonds are mainly divided into ionic bonds, covalent bonds and metallic bonds. Chemical bonds refer to the strong interaction between neighboring atoms. Ionic bond refers to the chemical bond formed by electrostatic interaction between anion and anion, covalent bond refers to the chemical bond formed by sharing electron pairs, and metallic bond refers to the strong interaction between metal cation and free electron.
2 Factors Affecting Adhesion
When confronted with an adhesion problem, don't jump to conclusions; consider it as a whole. Often when customers encounter problems with adhesion, the first consideration is the coating problem. As a coating supplier, it is necessary to help customers to analyze the problem, find out the causes of the problem, and persuade customers to accept and solve the problem together. The following diagram is a cross section diagram of a coated film on a substrate. Including substrate, substrate surface layer, coating film, coating film surface layer and interface. Any of these parts may have an effect on the adhesion problem. At the same time, adhesion problems do not go beyond this range.
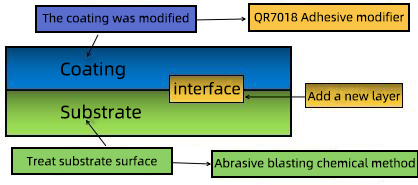
FIG. 1 cross section diagram of substrate coating structure above
Under normal conditions, the surface has good wetting, the two surfaces have good close contact, due to the above mentioned various forces, adhesion is not a problem. What is discussed here is what causes adhesion problems. According to the diagram above, we will discuss the possible problems in each part one by one.
2.1 Interface
If the substrate is a base coat, adhesion problems occur in the second coat. In addition, there is also the issue of re-coating adhesion, that is, the customer after spraying inspection surface defects, often not to remove the coating but to save time, directly re-coating once, resulting in adhesion problems. These conditions are likely to be due to the excessive amount of wax added to the recipe and the migration of wax to the first coated surface during baking can reduce the wax content to solve the problem. There is also a case of direct gas oven, gas combustion when the production of nitric oxide, nitrogen dioxide and sulfur compounds, these small molecules of the surface deposited on the bottom coating, the most serious is the second coating can be torn off like paper. If this is the case, the customer has no way to change the heating method of the baking oven. We can help the customer to try adding antioxidant to the formula to solve the problem. Also by the way is in the spraying of light paint, this direct combustion furnace produced compounds will also affect the color of coating film, mainly yellow. In addition to these small molecular compounds affecting adhesion, interfaces may also have stress effects. Liquid coating on the surface of the substrate wetting is easier than powder coating melt, powder coating itself expansion wetting is not very good, coupled with a certain degree of thermal stress when curing, so the test adhesion should be placed for a period of time, let the thermal stress disappear after the test. In addition, when the metal surface spray curing after cooling, metal substrate and the film thermal expansion and contraction speed is out of sync will also produce stress. If a workpiece is thick or thin, after baking and then quenching, the thin part of the substrate will cool faster, may be caused by stress adhesion problems
2.2 Substrate Surface Layer
Here mainly discusses the metal substrate surface layer. There has been a case, there is no pre-treatment aluminum plate adhesion is not up to standard, and in the pre-treatment aluminum plate surface adhesion up to standard. The reason is that a layer of oxide is produced on the surface of the aluminum plate without pre-treatment. This thin oxide layer is a weak oxide layer that affects the adhesion.
If the metal base material before treatment is not qualified, there may still be oxidation or rust reaction after the completion of spraying, although the coating can shield oxygen and water. When the coating film is not thick enough (the general polymer film below 60 microns may also produce oxygen and water vapor infiltration, equivalent to semi-permeable membrane), or there are channels formed by pinhole so that oxygen and water vapor can reach the interface. So after a period of time, there was a problem with adhesion. This can actually be detected by salt spray tests. So the metal surface pretreatment is very important, one is to remove the weak surface layer, two is the surface treatment layer itself can not become a weak surface layer, three is to surface passivation, no longer oxidation rust to continue to form a weak surface layer.
2.3 Coated Film Surface Layer
In addition to the aforementioned wax migration to the interface, there are also additives in the formulation, or small monomers or additives that are not removed from the resin itself, which may also migrate to the surface layer. This kind of circumstance needs to consider more in plastic surface bonding, in powder coating field is relatively rare, so do not discuss more here.
2.4 Coating Layer
Due to the curing temperature or time is not enough, the film did not cure completely, the film itself strength is not enough, when doing the grid test, the result adhesion. It is also possible that the coating is over-cured and the cross-linking density of the system is very high, such as polyurethane system. The coating itself is too brittle and the adhesion during the marking test is not high.
If after a period of time test adhesion, however, may be the coating weatherability is not enough, coating polymer in the light cracking or even powder lead to adhesion test.
2.5 Base Material Layer
The metal substrate surface layer was discussed previously, but the metal substrate layer usually has no effect on adhesion. The bottom coating discussed here as a substrate to consider, especially transparent powder light.
If bottom besmear itself is not resistant to weather, transparent pink does not cover. After a period of time, the primer itself cracking powder will cause adhesion test however. Sometimes although there is a layer of other coating in the middle, but very thin cover is not enough, after a period of time may also produce adhesion test not.
3、Test Method
National standard (basically the same as ISO) and American standard once had a customer complain about adhesion problem, they tested our products on their substrate adhesion, however, we did not have any problem with our own test, they tested the method I compare to the way we used to use ox plough.
Finally, I invited the quality director of their head office to come over and tested by him personally. No problem was found. It is even possible to plough a piece out of the ground. So you have to have standards, you have to adhere to standards, so that you can get comparable results.
According to the standard, there are two standard delimiting tool and manual delimiting, manual delimiting with interval guide device, there are a few points to pay attention to:
(1)Make sure the blade is in good condition;
(2)The knife should be drawn perpendicular to the surface of the pattern;
(3)Apply the force evenly, with a uniform rate of marking;
(4)Spacing according to film thickness: 0-60 muon hard substrate, 1mm spacing; 0-60 microns, soft substrate, 2mm spacing; 61-120 microns, hard or soft substrate, 2mm spacing; 121-250 microns, hard or soft, 3mm spacing;
(5)Use standard sellotape, keep the sellotape for reference after test. It can also be used to observe (with the aid of a magnifying glass), especially in multilayer systems, the adhesion of which layer to determine;
4、Conclusion
There may be a series of complex chemical reactions between film substrate and cross-linking and adhesion promotion in powder coatings. In this way, the adhesion modifier must match the resin and group of the film in the powder coating, because not every interaction is beneficial to the adhesion, QR7018 is a comprehensive solution to the adhesion modifier.